Draw A Water Molecule Include Its Polar Nature And How It Hydrogen Bonds With Other Water Molecules

But the carbon hydrogen c h bonds in the rest of the alcohol molecule are nonpolar.
Draw a water molecule include its polar nature and how it hydrogen bonds with other water molecules. If we look at a water molecule we can see the oxygen atom shares electrons. The slight negative charge near the oxygen atom attracts nearby hydrogen atoms from water or positive charged regions of other molecules. There are two lone pairs of electrons on each oxygen atom represented by.
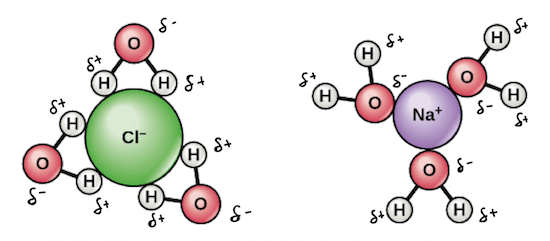
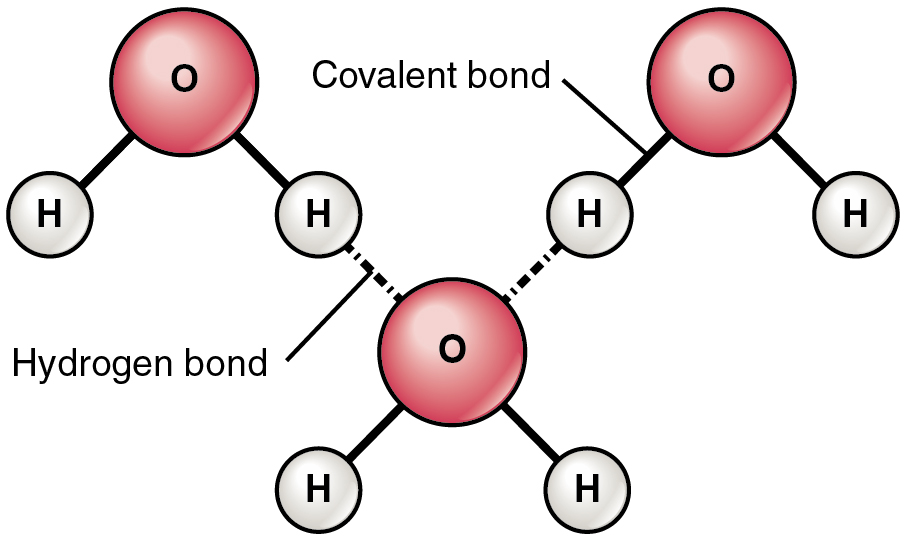
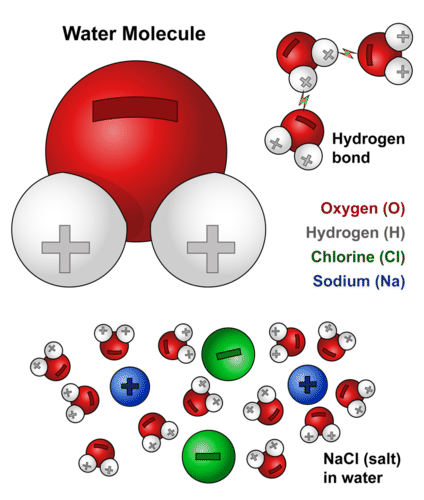
Water is found almost everywhere on earth and is required by all known life. Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. The bond is between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen atoms of another water molecule not between the two hydrogen atoms a common misconception how this works is that the polar nature of the water molecule means each hydrogen atom experiences attraction to both the oxygen it s bound to and to the non hydrogen.
Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form a relatively high boiling point of 100 c for its molar mass and. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids thus dissolving them. Water h 2 o.
Remind students that the oxygen hydrogen o h bonds in water make it a polar molecule. The water molecule chemical and physical properties. Water is a chemical compound and polar molecule which is liquid at standard temperature and pressure.
Water is an excellent example of hydrogen bonding. Water h2o should be drawn as two hydrogen atoms connected to one oxygen atom by a bond known as a polar covalent bond. Hydrogen bonds are the result of an unequal charge distribution on a molecule these molecules are said to be polar.
This polarity makes water molecules attracted to each other. The shape of each water molecule influences the way it interacts with other water molecules and with other substances.