Draw A Model Of Your Cell Using Arrows To Indicate The Direction Of Movement Of Each Substance
Label the diagrams below using glucose starch water iodine to identify the contents of the cell and the beaker in the initial state and in the final state of the experiment.
Draw a model of your cell using arrows to indicate the direction of movement of each substance. If it is moved passively use a blue arrow. Also in the final state diagram clearly draw arrows to indicate the movement of molecules during the experiment. Osmosis continue reading osmosis lab example 2.
B glucose is not synthesized by plants in the dark. Drag the arrows onto the diagram to show the direction of na gray arrows and k red arrows movement through each transport protein at resting potential. Diffusion is the random movement of molecules to an area of lower concentration from an area of higher concentration.
Explain the reason key. Some of the latitude and longitude lines have been labeled. A method of active transport across the cell membrane in which the cell takes in extra cellular fluids including its molecules e g.
Then draw a model of your cell using arrows to indicate the direction of movement of each substance. If no ions move through a transport protein at resting potential leave that target blank. Points a and b represent locations on earth s.
For each substance that moves through the plasma membrane draw an arrow indicating its most likely direction of movement into or out of the cell. Osmosis diffusion introduction. Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the diagram below which shows earth as seen from above the north pole.
Initial state final state figure 2. Diffusion is the result of this contact. A voltaic cell also known as a galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity.
For the process of photosynthesis the arrow labeled a would most likely represent the direction of movement of a light is needed for the process of reproduction. Movement of substances may occur from higher to lower concentrations down the concentration gradient or from the opposite direction up or against the gradient. If it is moved actively use a red arrow.
Now add arrows to figure 3 3 as instructed next. Review the chemical nature of each substance. Kinetic energy a source of energy stored in cells causes molecules to bump into each other and move in new directions.
It consists of two separate half cells. The shaded portion represents the nighttime side of earth. Enables a cell to acquire bulk.
A half cell is composed of an electrode a strip of metal m within a solution containing m n ions in which m is any arbitrary metal. 39 the diagram below represents a plant cell. Sugar and protein receptor mediated endocytosis the movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in.
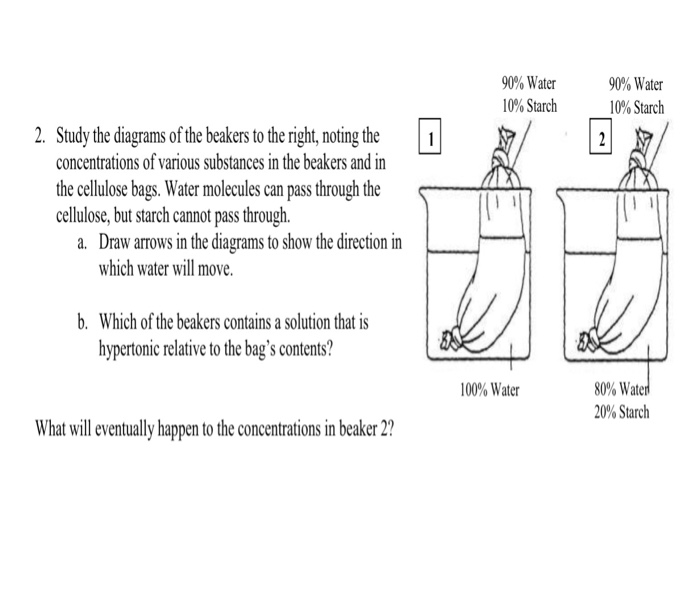
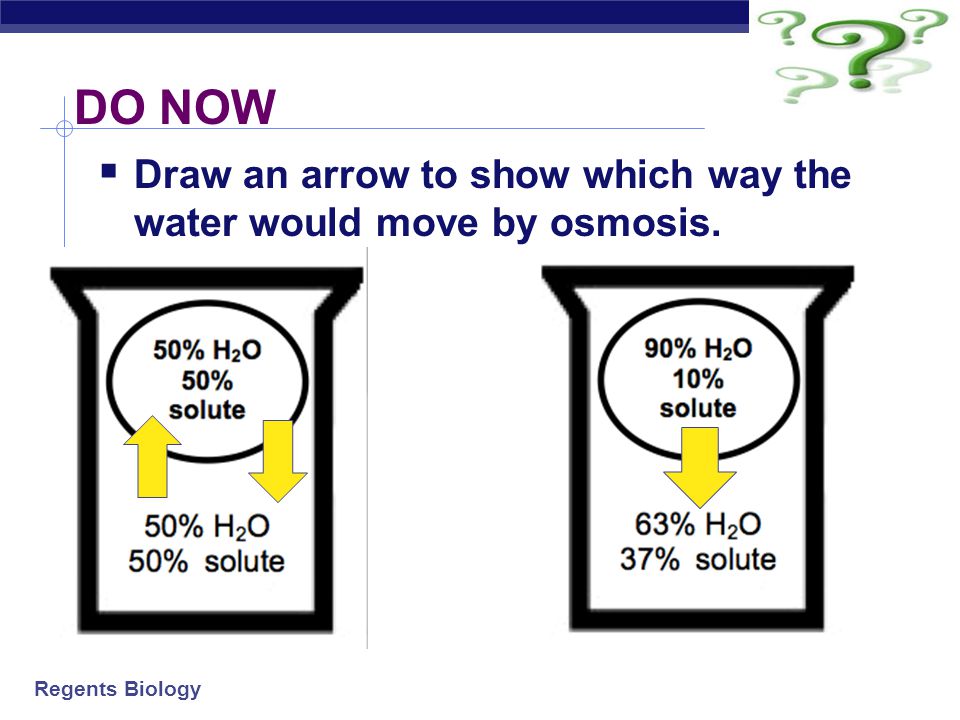
A solution may be hypertonic a higher concentration of solutes hypotonic a lower concentration of solutes or isotonic an equal concentration of solutes compared to another region.